Relation Between Post Stroke Depression (PSD) and CT- Scan and MRI Findings and Estimation of Functional Degradation in Patients 2-7 Months after Stroke
Juniper Publishers- Journal of complementary medicine
Abstract
Background: Stroke is a syndrome characterized by acute onset of neurological symptoms for more than 24 hours. PSD is the most common mood disorder in patients that its prevalence in women was more than men. The aim of this study was to determine the relation between PSD and CT-scan and MRI findings and the degree of functional degradation in patients after the stroke.
Methods: This descriptive-analytical study was performed on patients with stroke. All of them had depression based on Beck’s depression test. Necessary information including cardiovascular risk factors, type of ischemia, involved hemisphere, involved artery and extent of conflict were recorded in a checklist and the functional degradation in patients is calculated by scores of the Modified Rankin Scale (MRS). Collected data analyzed by statistical methods in SPSS version 21.
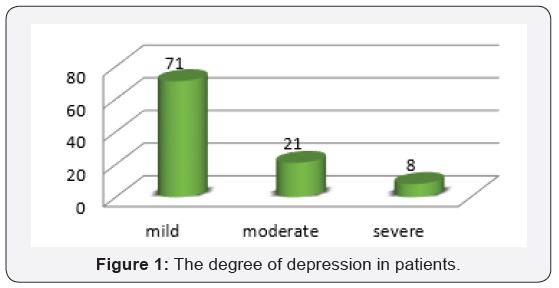
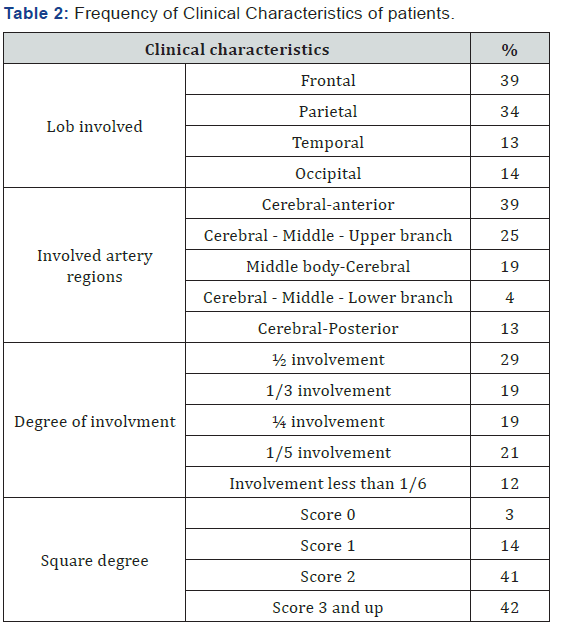
Results: In this study, 100 patients (43 males and 57 females with an average age of 63.97 years) were studied. Of all patients, 71% had mild depression. Of all patients, 80% had ischemic lesions, 56% had involvement in right hemisphere, 39% in frontal and 39% in the cerebral- anterior.
Conclusion: The results showed that depression in women is more than men. The prevalent degree of depression was mild, the form of stroke was ischemic type and the most area involved was right hemisphere of the brain.
Keywords: Stroke; Depression; Ischemia; Hemorrhage
Introduction
Cerebrovascular disease is an acute neuropathic disorder caused by abnormal blood flow to a part of the brain tissue that occur due to brain vessel obstruction as a result of blood coagulate or a rupture one of its feeding vessels. Post stroke depression is the most common and important neuropsychiatric consequences of stroke, which can result in longer hospital stay, compromise the effectiveness of rehabilitation, and reduce the patient’s quality of life [1]. According to the WHO report, the four main reasons for mortality in 2030 will be heart failure, stroke, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and lower respiratory tract infections. Stroke is a non-communicable disease among the elderly population that is the third leading cause of death in developed countries after coronary artery diseases and cancers [2]. The stroke is divided into two types of ischemic and hemorrhagic. Ischemic type is the most common cause of strokeand caused by formation of a localized clot or an embolism from another place such as the heart.3 Multiple risk factors such as systolic and diastolic hypertension, hypercholesterolemia , using smoking , alcohol and oral contraceptive pills, diabetes, and genetic factors have main role in the incidence of stroke but most of the strokes are multi factorial which influenced by polygenic and environmental factors [3]. The occurrence of stroke leads to occupational, social and mood disorders in patients. The PSD is the most common mood disorder in patients with stroke. The prevalence of PSD is estimated to be about 41.3% [4-5]. Depression is one of the disabling psychological complications of stroke which has devastating effects on all social, occupational, interpersonal, emotional and cognitive aspects of patients. PSD is common and several risk factors such as the location of the lesions in the left hemisphere, female gender, younger agegroup, history of depression and stroke and being alone are related to PSD. The most likely occurrence of depression occur in the first 2 years after stroke and its pick is in the first 3 to 6 months [6-7]. Some of studies have suggested depression as the main cause of death in stroke patients.7 Also female gender , age less than 60 years old , live alone, divorce, alcoholism , inability to return to work, decreased social activity , change in communication with others and size of brain lesions are the risk factors for post stroke depression [4,6-7]. Studies have shown that the use of antidepressants has reduced the incidence of stroke complications and improved its outcome. Therefore, timely diagnosis of depression and quick actions in its treatment are effective in reducing recurrence of stroke, mortality and improving the quality of life of patients [6,8]. Considering the importance of post stroke depression in the prognosis of patients and its mortality and also considering the burden of disease, the aim of this study was to investigate the relation between PSD and CT-scan and MRI findings and estimation of functional degradation in patients 2 to 7 months after stroke.
Method
This descriptive analytical study was done on 100 patients with post stroke depression who hospitalized in the neurology department of Alawi hospital in Ardabil city in 2016. Stroke confirmation was performed by a neurologist based on clinical symptoms and imaging. We used beck questionnaire included 21 questions about physical, behavioral and cognitive symptoms of depression. The questions in this questionnaire were scored based on 0-3 and the degrees of depression were classified from mild to severe. To determine the degree of functional degradation (degree of disability and dependency) we used Modified Rankin Scale (MRS) which included 6 questions with a score of 0-6. The collected data were analyzed by statistical methods in SPSS version 17.
Results
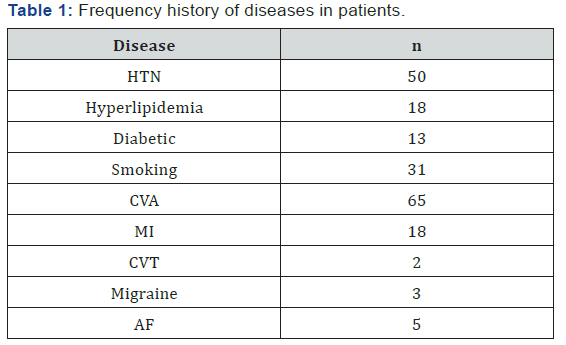
Of all patients, 57% were female and the rest were male. 77% of the patients were over 50 years of age and the average age of the patients were 63.14 ± 14.67 years (range 32-86). In 80% of patients the stroke was ischemic, and the rest was hemorrhagic. 56% of the patients had right hemisphere involvement and the rest of them had left hemisphere involvement. 71% of patients had mild depression (Figure 1). 18% of patients had a historyof myocardial infarction, 50% hypertension and 65% had CVA for the first time (Table 1). The results showed that the most involved lob was the frontal lobe and the most involved artery was the cerebral- anterior region with 39%, respectively. In 29% of patients, 50% of the brain pathway was damaged. The average score of MRS in patients was 2.53±1.25 and the highest degree of disability and dependency was related to score 2 with 41% (Table 2).







Comments
Post a Comment