In-Vitro Studies of Bio-Silver Nanoparticles in Cytotoxicity and Anti- Inflammatory- Juniper Publishers
Juniper Publishers-Journal of Complementary Medicine
Introduction
Nowadays, nanotechnology is a most promising
amphitheatre for generating new applications in biotechnology and
Nanomedicine [1]. Among several nanoproducts, a most prominent
nanoproduct is nano silver. Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) have become
increasingly popular as an antibiotic agent in textiles and wound
dressings, medical devices and appliances, such as refrigerators and
washing machines [2]. AgNPs have been used for antimicrobial,
antifungal, antioxidant, anticancer, and anti-inflammatory effects [3].
Green chemistry/Green synthesis is the design of
chemical products or process that minimize the use hazardous chemical
products and eliminate the environmental pollution. Therefore, green
synthesis of metallic nanoparticles from biological sources instead of
any other chemical products and from different methodologies is the
promising and challenging field. Due to this reason, biological method
has been prepared not only that it’s simple but cost effective too.
In several reports it is reported biological
synthesis of silver nanoparticles by plants and their antimicrobial
studies, but here the divergent attitude of mycosynthesis of silver
nanoparticles by mushrooms, especially medicinal mushroom such as Ganoderma lucidum and their anti-inflammatory and cytotoxicity studies.
Several diversity of naturally occurring mushrooms is
found to have promising antioxidant and anticancer properties and
prolong the longevity [4]. Mushrooms are mostly known to have
anti-inflammatory, cardiovascular, antitumor, antiviral, antibacterial,
hepatoprotective and hypotensive activities in biological systems [5-7].
Studies in the edible and medicinal mushroom has revealed lots of
beneficial therapeutic properties of them. In our study Ganoderma lucidum
(Fr.) Karst. (Ganodermataceae),basidiomycetous fungi, has been widely
used for the general promotion of health and longevity
in Asian countries for centuries [8]. This edible mushroom
was considered to preserve the human vitality and to promote longevity
not only that the dried powder of mushroom was used as a cancer
chemotherapy agent in ancient China [9]. In addition, Ganoderma lucidum
has been used to treat various other disorders such as allergy,
arthritis, bronchitis,gastric ulcer, hyperglycemia, hypertension,
chronic hepatitis, hepatopathy, insomnia, nephritis,
neurasthenia,scleroderma, inflammation, and cancer [10-14].
Materials and Methods
Extraction of mushroom extract
Ganoderma lucidum mushroom obtained was washed several times with deionized water.
68g of finely blended sample was boiled for 2-5min in
300mL water and filtered. The filtrate is cooled to room temperature
and used as reducing agent and stabilizer [15].
Synthesis of AgNPs
35mg AgNO3 is dissolved in 250mL water. To obtain
silver colloids 6ml of mushroom was added in 30ml of AgNO3 solution. The
formation of Ag nanoparticles is indicated by light yellow-brown colour
and the reduction is completed in 30m. The formation of nanoparticles
was examined under UV-visible spectrophotometer [15].
Characterization of the nanoparticles
The particle was characterized by UV-visible studies
for preliminary confirmation, and the particles were subjected to HR-TEM
studies for their size determination, EDAX to determine the percentage
of metals present and XRD was done for determination of size and
crystalline nature.
Human ethic clearance
All procedures involving human samples were strictly
conducted in accordance with approved guidelines by the Institutional
Human Ethics Committee (Ref No: FLL/
IEC/04/2014) by Frontier Lifeline Hospital - Institutional Ethics
Committee (Ref: FLLH-IEC, Reg No: ECR/200/INST/TN/2013)
and in accordance to the regulatory guidelines prescribed
by Ethical Guidelines for Biomedical Research on Human
participants, ICMR, 2006; Good Clinical Practice & Guidelines
for Clinical Trials on Pharmaceutical products in India, CDSCO,
DGHS, MoHFW, Govt of India, including Schedule Y 2005 and its
revisions.
In-vitro anti-inflammatory
Membrane Stabilization assay
Preparation of haemoglobin rich red blood cells suspension:
The blood was collected from healthy human voluntary who has
not taken any NSAIDs (Non steroidal antiinflammatorry drugs
) for two weeks prior to the experiment and transferred to the
centrifuge tubes.It was centrifuged at 3000rpm for 10 min
and were washed three times with equal volume of saline.The
volume of the blood was measured and reconstructed with 10%
V/V suspension with normal saline [16-18].
Heat induced haemolysis assay: The reaction mixture
2ml (Sample A and sample B ) consisted of 1ml of test sample
of different concentration (1.4,4.32,8.64,12.9,14.4,21.6 mg/l)
and 1ml of 10% hRBCs suspension ,instead of test sample
only saline was added to the control test tube.Aspirin (100μg/
ml) was used as standard drug.All the test tube containing
reaction mixture was incubated in water bath at 56 0C for 30
minutes.After the incubation,it was cooled for 5min.Then the
reaction mixture was centrifuged at 2500 rpm for 5 min and the
absorbance of the supernatant was taken at 560nm using UVVis
spectrophotometer [19,20]. The experiment was performed
in triplicates and percentage inhibition of haemolysis was
calculated as follows;
Percentage inhibition=(Abs control-Abs sample)X 100/Abs control
Hypotonicity induced haemolysis assay: The reaction
mixture 3ml (Sample A and B) consisted of 0.5ml of different
concentration (1.4,4.32,8.64,12.9,14.4,21.6mg/l) and 2ml of
hyposaline,0.5ml hRBCs suspension,in control test tube instead
of test sample 0.5ml of phosphate buffer was added.Diclofenac
sodium (100μg/ml) was used as standard drug. All the test tube
were incubated at 37 0C for 30 minutes and centrifuged at 3000
rpm for 10 min.The absorbance of supernatant was taken at
560nm using UV-Vis spectrophotometer [21]. The percentage
inhibition of haemolysis was calculated as follows;
Percentage inhibition=(Abs control-Abs sample)X 100/Abs control
Protein denaturation
Inhibition of Albumin denaturation: The equal amount
of 3ml reaction mixture (0.2ml egg albumin + 2.8ml phosphate
buffer saline) was added to different concentration of test
sample and make up the 2 ml of distilled water. In control test
tube instead of test sample, PBS was added.Aspirin (100μg/ml)
was used as standard drug. All the test tube were incubated at
370C for 15 minutes and incubated at 70 0C for 10 minutes. The
samples were cooled for 5 minutes and absorbance was noted
at 660nm using UV-Vis spectrophotometer [22]. The percentage
inhibition of albumin denaturation was calculated as follows;
Percentage inhibition=(Abs control-Abs sample)X 100/Abs control
Inhibition of BSA denaturation: The equal amount of
450μl BSA(1mg/ml) was added in different concentration
(10,30,60,90,120,150μl/ml) of test samples and made up
into 1ml of distilled water. All the rest of steps were followed
according to the albumin denaturation [22].
Percentage inhibition=(Abs control-Abs sample)X 100/Abs control
Proteinase inhibition assay: The test followed according
to the modified method of [21]. The reaction mixture (2ml)
containing 6μl trypsin, 1ml (20mM) tris HCl and along with
different concentration of test samples.The mixture was
incubated at 37 oC for 5 min after that 1 ml of 0.8% (w/v) casein
was added. The mixture was incubated again for 20min, 2ml
(70%) perchloric acid was added to arrest the reaction. Cloudy
suspension was observed,it was centrifuged for 5 min and the
supernatant was read at 210 nm using UV-Vis spectrophotometer.
Control was run as same procedure but instead of test sample
PBS was suspended [21]. The percentage of inhibition of
antiprotienase was calculated as follows;
Percentage inhibition=(Abs control-Abs sample)X 100/Abs control
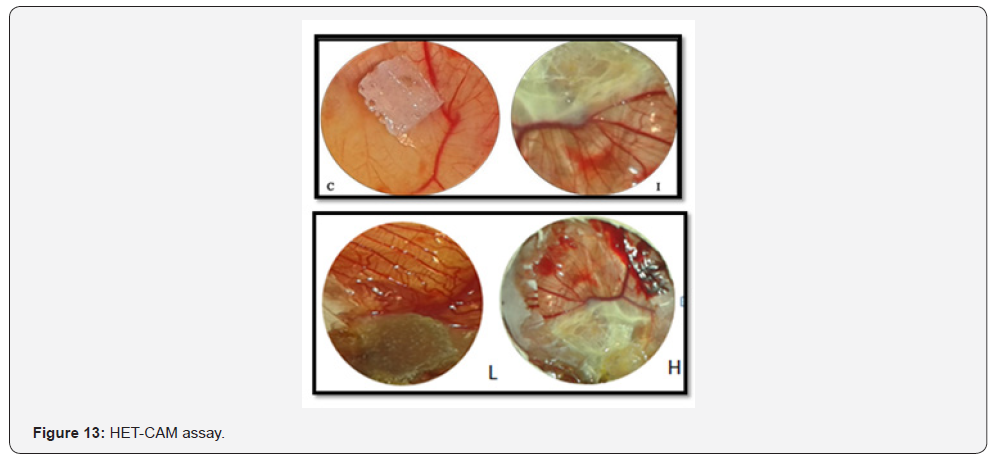
HET- CAM assay
Pellet preparation: 7.25mg sodium dodecyl sulfate was
dissolved with or without concentration of chitosan and
sacchachitosan transdermal films in 1ml of agarose solution.
10μl of gelling solution was used for pellet preparation.
Incubation [22,23]: The fertile hen eggs were incubated for
75h at 37 °C and relative humidity of 80%.The eggs were kept
in horizontal position and rotated several times. Then open
snub end after aspiration of 10ml of albumin from hole. Eggs
were traced with scalpel and thereafter the shells were removed
with forceps. One pellet per egg was put on newly formed
chorio-allanthoic membrane, agarose pellet without SDS acts as
negative control, agarose pellet with SDS acts as positive control
and agarose pellet with SDS and tested sample acts as treatment.
The aperture was covered with parafilm and eggs were returned
into the incubator for 24h of incubation.
Interpretation [24]: The inhibition or membrane irritation
was observed. Positive control egg, exist if the irritation of
membrane induced by SDS. Negative control egg, exist no
irritation of membrane. Treated group egg, exist various
irritation according to concentrations used.
Three irritation reactions such as hemorrhage, lysis and
coagulation were monitored and image was taken with the help
of SONY 14.1megapixels video camera at 35cm above CAM.
Time was recorded in seconds, from addition of SDS until the appearance of three irritation reaction.
Calculation [25,26]: Irritation index was calculated using
following e equation.
IR=300x(IR)=5x(301-TL)+9x(301-TC)
Time (T) of hemorrhage (H), lysis (L), and coagulation (C)
during a period of observation of 300 seconds. IR can take values
between 0 and 21.
Relationship of starting irritation reaction was denoted by
H’, L’, and C’.
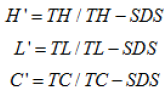
Antioxidant assay
DPPH assay: The free radical scavenging activity of the
fraction was measured in vitro by 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl
(DPPH) assay.About 0.3 \mM solution of DPPH in ethanol was
prepared and 1ml of this solution was added to 3 ml of the fraction
dissolved in ethanol at different concentration.The mixture was
thoroughly mixed,incubated at RT for 30 minutes.Then the
reading was taken at 517 nm using UV-Vis spectrophotometer
[27]. Ascorbic acid was used as standard drug.The percentage of
inhibition of DPPH was calculated as follows;
Percentage inhibition=(Abs control-Abs sample)X 100/Abs control
Lipid peroxidation assay: Liver was obtained and
homogenized using phosphate buffer. Reaction mixture I
consists of 1ml liver homogenized(10% W/V),1 ml different
concentration of test sample.Lipid peroxidation was induced by
100μl (15mM) ferrous sulphate.Its incubated for 30 minutes at
RT.0.1ml reaction mixture II (1% SDS & 0.1% thiobarbutric acid)
added to all test tube and made up to 1 ml with distilled water
and incubated for 1 hour at 95 oC, After butanol and pyridine was
added in the ratio 2:1. The reaction was mixed thoroughly and
centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 15 minutes to separate the layers.
Organic layer was separated and read at 530nm using UV-Vis
spectrophotometer [28]. The percentage of inhibition of lipid
peroxidation was calculated as follows;
Percentage inhibition=(Abs control-Abs sample)X 100/Abs control
Cytotoxicity assay
Cell Line and Culture Conditions: Vero and HeLa
cell line were purchased from the virology dept of king’s
institute,Guindy,chennai . The cancer cell line was maintained
in RPMI-1640 culture medium supplemented with 10% fetal
bovine serum, 100μg/ml penicillin and 100 μg/ml streptomycin
in a 5% carbon dioxide (CO2) cell incubator at 37 °C
MTT assay: The 3-(4, 5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,
5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide dye reduction assay was
performed to determine the cytotoxic effect of the AgNPs at
various concentrations. The assay depends on the reduction of
MTT by mitochondrial dehydrogenase, an enzyme present in the
mitochondria of viable cells, to a blue formazan product. The cell
concentration was adjusted to 1 × 105 cells/ml and plated onto
96-well flat bottom culture plates with various concentrations
of AgNPs. All cultures were incubated for 24 hours at 37 °C in
a humidified incubator. After 24 hours of incubation (37 °C, 5%
CO2 in a humid atmosphere), 10ml of MTT (5mg/ml in PBS) was
added to each well, and the plate was incubated for a further
four hours at 37 °C. The resulting formazan was dissolved in
100 ml of dissolving buffer (provided as part of the kit) and
absorbance of the solution was read at 595nm using an Elisa
reader. All determinations were carried out in triplicate [29].
Concentrations of AgNPs showing 50% reduction in cell viability
(i.e., IC50 values) was then calculated.
Apoptosis Assay - Ethidium Bromide / Acridine Orange
Staining: The cells were stained to assess the level of apoptosis
[30]. After the treatment period the cells were trypsinized and
isolated. 25μl of cell suspension was mixed with 5μl acridine
orange and 5μl of ethidium bromide. 10μl of the mixture was
added to frosted glass slides and viewed under fluorescent
microscope immediately. Cells were analyzed in fluorescent
microscopy under 10X objective.
Statistical analysis
Data pertaining to antioxidants and anti-inflammations
of silver nanoparticles were expressed as mean ± SEM, n = 6
and the data were analyzed by One-way ANOVA using GraphPad
Prism version 6.00 for Windows (GraphPad Software, La Jolla
California, USA). In all the analysis, P < 0.05 was considered as
statistically significant.
Results and Discussions
The study on biological synthesis of silver nanoparticles
has been previously reported by us [31]. Further applications
and cytotoxicity of synthesized silver nanoparticles has been
reported in this work.The synthesis of silver nanoparticles from
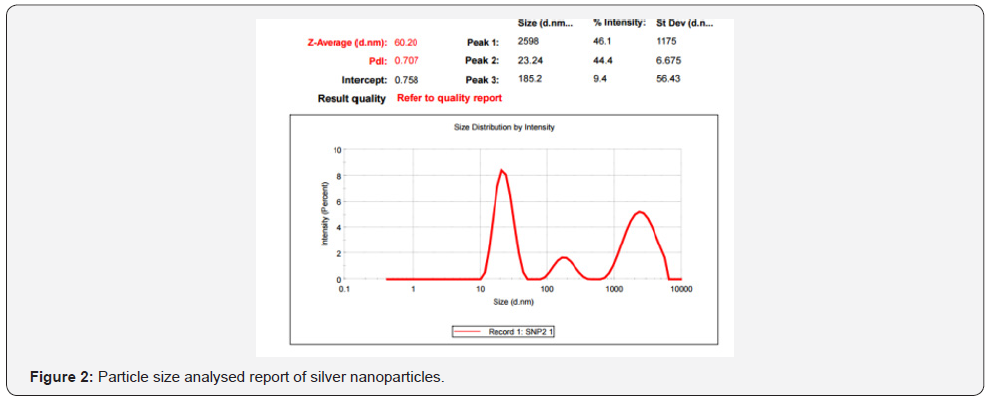
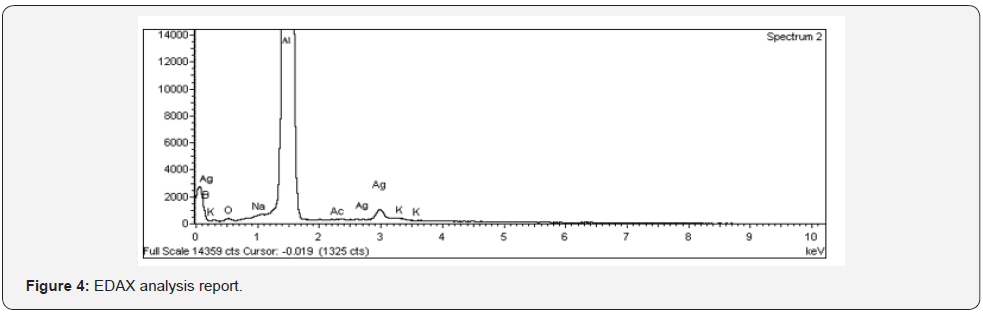
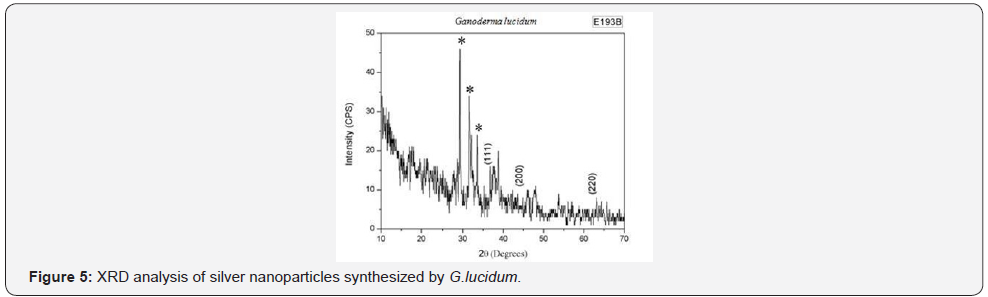
Ganoderma lucidum was confirmed and characterized by various
analytical techniques such as UV-VIS spectroscopy,HR-TEM,ICPOES,
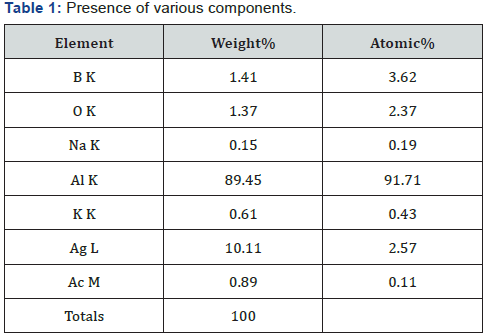
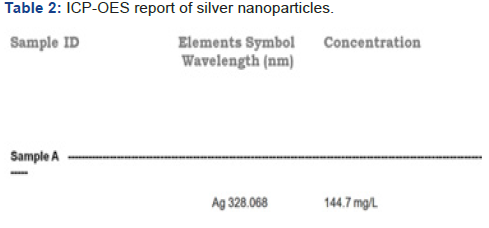
XRD,EDAX and SAED (Figure 1-5, Table 1 & 2 ).


Several concentration ranging from 1ssmg to 21.6mg of
synthesized silver nanoparticles sample was tested for their
antioxidant activity in different in-vitro models. It was observed
that free radical scavenged by the sample (standard.Ascorbic
acid and tested.Silver nanoparticles) in their unique percentage
of inhibition in a concentration dependent manner. Figure 6-7
reveals the reductive capacity of tested samples compared to
that of standard [32-35].
In the DPPH method, the antioxidants present in the silver
nanoparticles reacts with the stable DPPH (deep violet colour)
and converts it into 1, 1 diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazine with
discoloration. In the present study, the percentage of inhibition
of free radicals at different concentrations ranging from 1-21.6
mg for the tested samples was calculated and compared with
the standard ascorbic acid and the results are revealed in
Figure 6. This is the common and successfully used method
for investigating both hydrophilic and lipophilic antioxidant
properties [36-38]. The inhibitory effect (IC-50) follows, SNPs
(9.0±.001mg/ml) and Std. Ascorbic acid (7.0±.003mg/ml)
respectively. The prominent results were observed with the
Bio-silver nanoparticles that may be due to synergy effect of
components such as Ganoderma lucidum and silver nanoparticles
comparable to standard ascorbic acid.

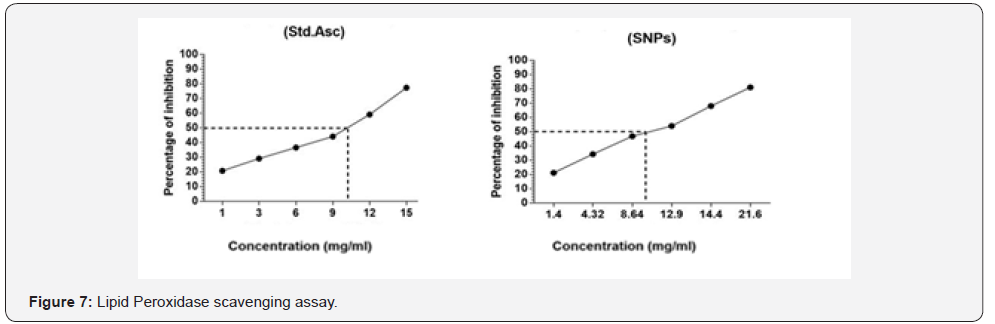
Lipid peroxidation is a critical procedure in free radical
pathology as it is cause damage to cells. The liver of hen
was utilized as a source of polyunsaturated unsaturated
fats for determining the degree of lipid peroxidation [39].
Malondialdehyde is lipid peroxidation product is a pointer
of receptive oxygen species (ROS) generation in the tissue restraint of lipid peroxide development by tested sample (silver
nanoparticles) and standard (ascorbic acid) appeared in Figure
7.
Anti-inflammatory assays
The HRBC membrane stabilization is one of the techniques
followed to study the anti-inflammatory activity. Erythrocytes
membrane is closely resemblance of lysosomal membrane
[40,41]. Furthermore, stabilization of the lysosomal membrane
depends on the sample and the concentrate, stabilization of
lysosomal membrane is vital in constraining the inflammation
response by preventing the release of initiated neutrophil,
for example, bacterial proteins and proteases, which creates
additional tissue irritation and damage upon extracellular
discharge. The enzyme released during response results in
various disorder especially with chronic and acute inflammation.
The role of drug administrated showed the inhibition and
stabilization of lysosomal membrane.
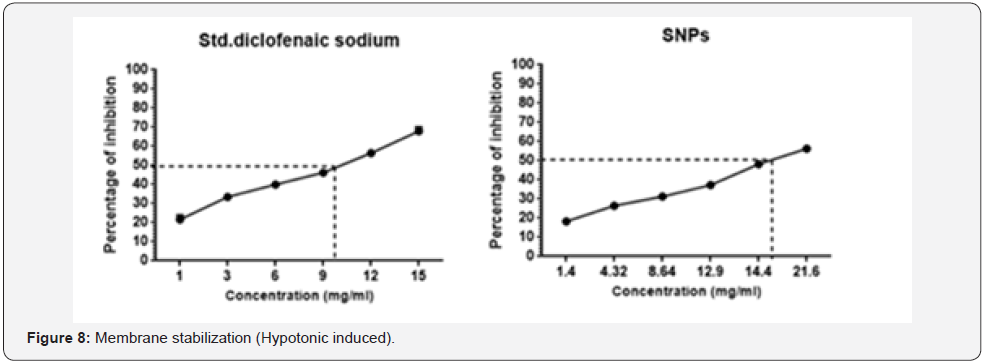
The inhibition of hypotonicity induced HRBC membrane
lysis and the stabilization of the membrane by tested sample
(silver nanoparticles) and standard sample (Diclofenac sodium)
was taken as the measure of anti-inflammatory activity. The
percentage of inhibiting lysis of membrane depends on tested
sample,it was depended on concentration gradient the tested
sample (Silver nanoparticles) were significant (P<0.05) to that
of standard drug and has been illustrated at Figure 8. Silver
nanoparticles showed the maximum protection of 58% at the
concentration 21.6mg, whereas diclofenac sodium showed 69%
at the concentration range of 15mg.
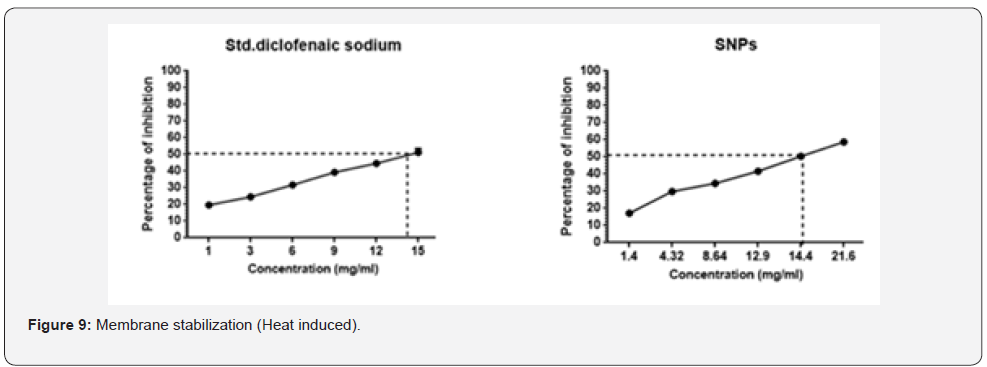
The tested samples were analysed to study the inhibiting
reaction against the membrane lysis. From the results observed
all the samples along with standard showed a good and
statistically significant (P<0.05) protection of erythrocyte
membrane from damage. The detailed report has been analysed
and reported at Figure 9.
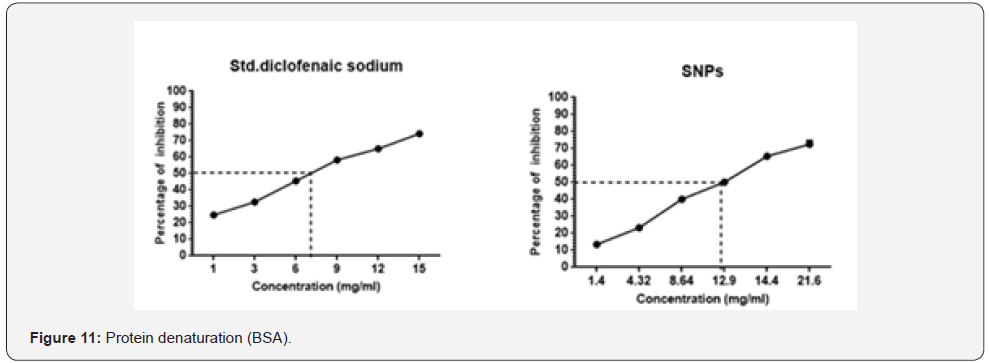
Protein denaturation is technique in which the protein
loses their original form by the external stress or any other
chemical compounds [42]. It is one of main cause during the
inflammation process. As part of our investigation on the
anti-inflammatory mechanism, different concentration of test
sample along with standard were checked for the ability of
inhibiting protein denaturation. It was effective in inhibiting
the protein denaturation; checked with egg albumin and
maximum protection was seen in tested sample (sacchachitosan
transdermal film) 79.71% & 72.3% at the concentration range of 36.7mg/L, whereas 50% of inhibition was seen at range of
1-2mg/L, other samples shows the maximum inhibition activity
such as follows GL;50.1 & 49.86% (15mg/ml), SNPs; 70.06%
& 72.54% (21.6mg/ml), C; 64.32% & 67.63% (15mg/ml), Sc;
61.8 & 65.16% (15mg/ml) and CF; 73.24 & 73.23% (32.5mg/l)
compared with std. diclofenac sodium; 61.78 & 74.32% (15mg/
ml). Each value represented (Figure 10 &11) the average mean ±
SEM; N=6. All the samples were statistically compared with the
standard ****P<0.001 considered extremely significant (oneway
ANOVA followed by ordinary test was performed using
GraphPad Prism version 6).

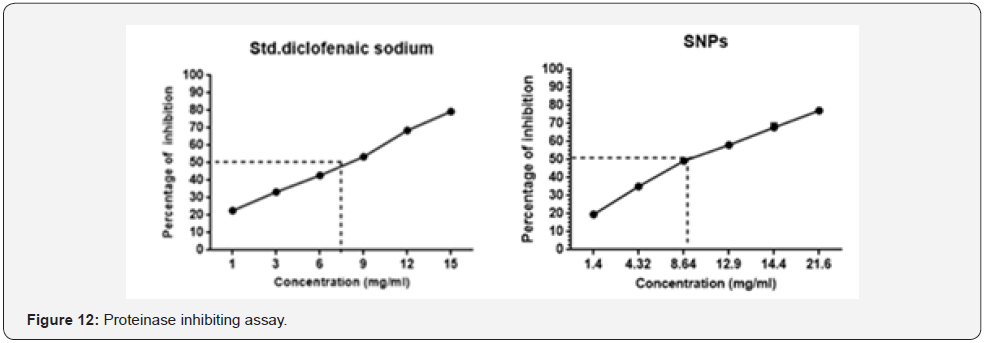
Serine proteinase is one of major enzyme released from
neutrophils and plays a vital role in the development of tissue
damage during inflammation response [43] and significant
protection was given by proteinase inhibitors. Samples such as
SNPs and standard diclofenaic sodium exhibited significant antiproteinase
activity at different concentrations as illustrated in Figure 12. Samples showed maximum inhibition of SNPs; 77.18%
(21.6mg/ml) and Diclofenac sodium; 74.36% (15mg/ml). It’s
significant ****P<0.001 with standard (diclofenac sodium).
HET-CAM assay is a unique model to analyse the antiinflammatory
role. The two concentrations such as low and high
concentration of silver nanoparticles was taken to analyze the
role of anti-inflammatory and the membrane irritation resistant.
Haemorrhage, lysis and coagulation are the different parameters
to be observed during this study.
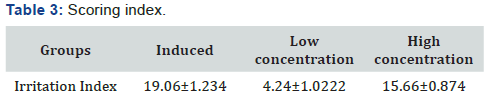
The inhibitions of irritant reaction in the group of
negative control (Induced-SDS) and in the treatment group
(silver nanoparticles-SDS) are subjected to chorioallantoic
membrane and the changes in CAM was observed and shown
at Figure 13. The mean time for the initial irritation reaction
in the membrane for each one from tested to control has been
calculated and shown (Table 3). From the results; it clearly
shows that low concentration gave less irritation compared to
higher concentration. There was significant statistical difference
between concentrations. Intensive studies of anti-inflammatory
analyses are carried by different researchers [44-46] in context
with different application. Accordingly, this study has revealed
the scientific justification that silver nanoparticles posses antiinflammatory
property. Hereby may be taken further for in-vivo
wound healing activity Figure 14.

Cytotoxicity assay
3-(4, 5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2, 5-diphenyl tetrazolium
bromide assay was performed to evaluate the cytotoxicity
effect of silver nanoparticles against the African green monkey
kidney cell (vero) and cervical cancer cell (HeLa). The different
concentrations of samples were used to determine the cell
viability after 24hrs incubation of cells with test samples. The cytotoxicity was dependent fully on concentration gradient
as the concentration increased mild toxicity was observed at
vero but in HeLa cytotoxicity level was higher and viability of
cells are lesser (14). The data was analysed by two-way ANOVA
followed by paired T tail test to determine significance difference
and correlation between samples. From the results, we have
observed that significant (P<0.05) difference and correlation
(P>0.05) between cell viability and cell inhibition. Similar kind
of studies was portrayed by [47], with different extract in to
compare toxicity.Further AO-EB staining was performed to
analysis the apotosis of cells, IC50 value (5.10±0.41mg/ml) of
silver nanoparticles in HeLa cells reveals almost 60% Figure 15.
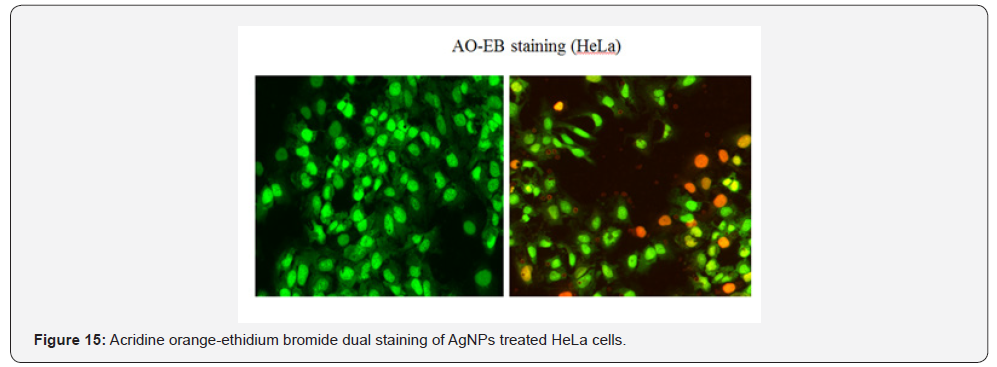
The apototosis and necrosis property of silver nanoparticles
was assesd by IC 50 value against HeLa cells using acridine orange
and ethidium bromide dual staining.It was incubated for 24h and
picture was taken with fluorensce microscope.The treated cells
showed early apoptotic cells with the appearance of fluorensce
green nuclei due to nuclear fragmentation and chromatin
condensation and necrotic cells indicated by orange coloured
cells due to the condensation of nuclei; nuclear shrinkage and
blebbing.Thus confirming apoptotic activity (see fig ). Similiar
kind of results were followed with different cancereous cells [48-
50]. On comparison, the untreated (control) cells showed green
color when stained with AO-EB, indicating their viability nature.
Conclusion
The outcomes of our research work demonstrated that the
biological synthesized silver nanoparticles have indicated less
toxicity impact on normal cell line than cancerous cell line and
have advocated the ramifications of silver nanoparticles in curing
inflammations and tumour suspected afflictions. Additionally
this investigation is a bench top model and may be explored
further for the anti-inflammatory and wound recuperating
application.
For more
articles please click on Journal of Complementary Medicine &
Alternative Healthcare




Comments
Post a Comment